In this article we will discuss about the potential and kinetic energy found in living cells.
Potential Energy:
It is considered as stored energy. It cannot produce a change but it has latent power, which, on release, is capable of doing work. The water in a lake on a mountain or in a dam does not do any work but it is under gravitational pull.
If the water is allowed to flow downwards it can move a machine or a turbine, the stored energy being released in down-flow. A piece of coal is inert but on burning the energy stored in it is converted into kinetic energy—heat and light.
Motion or Kinetic Energy:
The energy may be in the form of mechanical energy of a moving body. Heat and light are placed under this category. The energy source of earth is radiant energy from the sun. The green plants can synthesize organic molecules, sugar in the form of chemical energy, a kind of potential energy.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
In the process, carbon dioxide and water are joined by using sunlight as a source of energy. Light is absorbed in the chlorophyll pigment and transformed by the cells into the chemical energy needed for the synthesis of carbohydrate.
The radiant (kinetic) energy is transformed into chemical (potential) energy, which is stored in carbohydrate molecules. From simple inorganic compounds, plants can synthesize highly complex organic compounds, such as carbohydrates, fats and proteins and a considerable amount of energy is stored in these molecules.
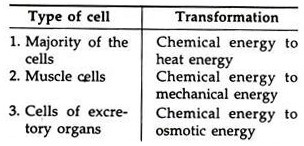
In the living cells, the food molecules are subjected to chemical reactions and the potential energy in the molecules change into heat, light, motion or some other kinetic energy. Energy is neither created nor destroyed but simply transformed from one form to another. Living cells are unique in their ability to transform chemical energy directly into heat energy, without being initiated by some other energy.
Energy Transformation in Living Cells