In this article we will discuss about:- 1. Biochemistry of Calcitonin 2. Biosynthesis of Calcitonin 3. Physiological Roles.
Biochemistry of Calcitonin:
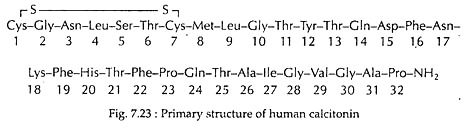
Calcitonin is peptide hormone having 32 amino acid residues, with a 1-7 intrachain disulfide ring and a prolinamide carboxy-terminal group (Fig. 7.23) in human.
Biosynthesis of Calcitonin:
Like many other peptide hormones, it is derived from a larger precursor molecule.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Regulation of secretion:
TSH cannot regulate calcitonin secretion from thyroid. The serum calcium levels when rises, there is a linear rise in CT secretion; fall in serum Ca2+ decreases its secretion. Besides serum Ca2+, other hormones like catecholamine, glucagon, gastrin, CCK, stimulate calcitonin secretion. Somatostatin inhibits its secretion.
Physiological Roles of Calcitonin:
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Calcitonin is a blood calcium regulating hormone. It decreases serum Ca2+ and PO43− levels by acting on osteoclast cells of bones and renal tubules. In pregnant and lactating women, growing children and egg-laying birds, CT plays an important role in Ca-regulation.
Effects on bones:
Calcitonin decreases blood calcium levels by inhibiting Ca2+ and Pi mobilisation from bones into the blood. In the bones, the osteoclasts are the bone resorping cells. In bones, CT decreases (i) the rufflings and microvilli on the membrane of osteoclasts, (ii) activities of lysosomal hydrolases, alkaline phosphatases and pyro-phosphatases and stimulates phosphate influx into bone cells.
All these activities lead to decreased bone resorption by osteoclasts, thus less Ca2+ is available in blood. This hormone also inhibits the Ca2+ mobilising action of PTH (parathyroid hormone) on osteoclasts, rather than promoting bone formation by osteoblasts.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Effects on renal tubules:
In the thick ascending limb of Henle’s loop and distal renal tubules (DCT), CT decreases the reabsorption of Ca2+ and Pi from the tubular filtrate. Thus, it enhances the renal excretion of calcium which may contribute to its hypocalcemic effect.