The following points highlight the fifteen main advantages of goat farming.
1. The initial investment needed for goat farming is low.
2. Due to small body size and docile nature, housing requirements and management problems with goats are less.
3. Goats are friendly animals and enjoy being with people.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
4. Goats are prolific breeders and achieve sexual maturity at the age of 10-12 months. It starts giving milk at the age of 16-17 months. Twining is very common, and triplets and quadruplets are rare.
5. In drought prone areas, risk of goat farming is very much less as compared to other livestock species.
6. Unlike large animals in commercial farm conditions, both male and female goats have equal value.
7. Goats are ideal for mixed species grazing. This animal can thrive well on wide variety of thorny bushes, weeds, crop residues, agricultural by-products unsuitable for human consumption.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
8. Under proper management, goats can improve and maintain grazing land and reduce bush encroachment (biological control) without causing harm to the environment.
9. In India, there is no religious taboo against goat slaughter and meat consumption.
10. Slaughter and dressing operation and meat disposal can be carried without much environmental problems.
11. The goat meat is more lean (low cholesterol) and relatively good for people who prefer low energy diet especially in summer and sometimes goat meat (chevon) is preferred over mutton because of its “chewability”.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
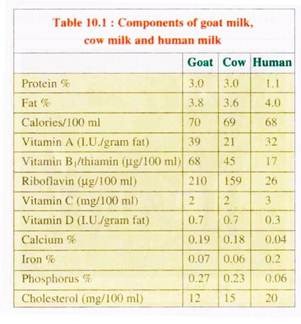
12. Goat milk is easy to digest than cow milk because of small fat globules and is naturally homogenised. Goat milk is said to play a role in improving appetite and digestive efficiency.
Goat milk is non-allergic as compared to cow milk and it has anti-fungal and anti-bacterial properties and can be used for treating urinogenital diseases of fungal origin. A comparative chart of components of goat, cow and human milk is given in Table 10.1.
13. Goats are 2.5 times more economical than sheep on free range grazing under semi-arid conditions.
14. Goat creates employment to the rural poor by utilising unpaid family labour. There is ample scope for establishing cottage industries, based on goat meat and milk products and value addition to skin and fibre.
15. Goat is termed as walking refrigerator for the storage of milk and can be milked number of times in a day.