The below mentioned article provides short notes on lac ecosystem.
In India, most of the lac host trees are confined in forest areas where the lac insect along with its host plants form an ecosystem. It is a complex multi- trophic web of flora and fauna, representing a rich biodiversity. It includes besides the lac insects, lac- host plants, several predators and parasites of lac insects, secondary parasites, microboes and a variety of pests of host plants.
In this ecosystem, the lac host plants constitute the first trophic level, lac insects and pests of host plants make the second, predators along with primary parasites of lac insect form the third and hyperparasites constitute the fourth trophic level.
Host plants: First trophic level:
ADVERTISEMENTS:
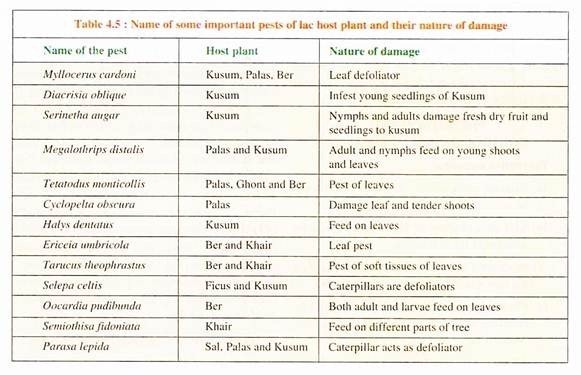
Lac insects require plant species for survival. More than 400 lac hosts have been observed to carry lac insects throughout the world. Important host plants available in our country were listed in Table 4.3.
Lac insects and pests of host plants: Second trophic level:
Nine genera and 87 species of lac insects are reported from the world. Most important and common lac insect species found in India include Laccifer (Kerria) lacca, L. albizziae, L.fici, L. indicola, L. longispina and L. sindica etc. In addition to lac insects, many other insects and organisms live on lac host plants. These include pests (see Table 4.5), birds and mammals.
Predators and parasites of lac insect: Third trophic level:
ADVERTISEMENTS:
In spite of the protective lac covering, the lac insect due to sedentary habit is always a sitting prey to predators and parasites. Twenty-two lac insect predators, 30 primary parasites, and several fungal as well as bacterial pathogens are known to present in lac ecosystem.
Hyperparasites: Fourth trophic level:
A number of arthropods (insects) often visit the lac encrustation which prey on or parasitise many important lac predators, thus comprising the fourth trophic level of lac ecosystem. These secondary parasites or hyperparasites are indirectly beneficial to lac cultivation in a way that they keep off the predator enemy insects.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Beneficial insects mostly belong to Chalcidae (Brachymeria tachardiae) (Fig. 4.26), Braconidae (Apanteles tachardiae, Chelonella cyclopyra), Elasmidae (Elasmus claripennis), Chneumonidae (Pristomerus sulci) (Fig. 4.27) and Bethylids (Perisierola pulveriae). They parasitise the eggs or larvae of Eublemma amabalis and Pseudohypatopa pulverea (see also biological control).
In lac ecosystem, some ants are always found which are the body guards of lac insects (Fig. 4.28). Again, few vertebrates (rat, squirrel etc.) attack lac cells during maturation time. Moreover, natural lac insect ecosystem maintains a variety of tree flora, macrofauna and soil micro-organisms.