The below mentioned article provides short notes on lac host plants.
The plants on which lac insects thrive by sucking phloem sap from succulent twigs are called lac host plants. Till date, more than 120 plants have been recognised as host plants, but the lac insect is a natural pest on these plants.
However, they are not treated as pests as such, because:
(1) They yield most useful product,
ADVERTISEMENTS:
(2) The host plants are economically not so important and
(3) The insects cause temporary and recoverable damage to the host plants.
What factors distinguish host plants from non-host plants are not exactly determined.
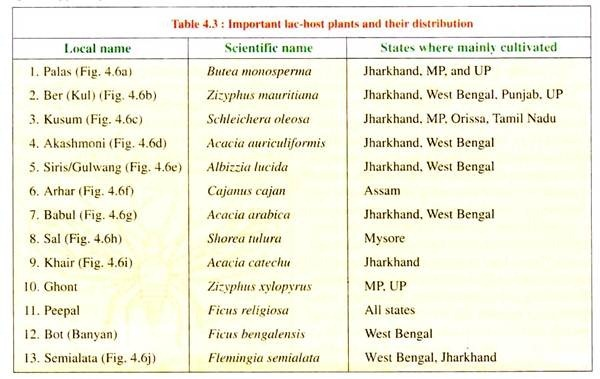
It is assumed that phloem saps of all known host plants have pH ranging from 5.9-6.2 and density from 0.14-0.17. Among the host plants, some serve as hosts only in certain areas but not in others. For example, ‘Arhar’ in Assam and ‘Ghont’ in M P. The name of major host plants of lac insect found in India are given in Table 4.3 (Fig. 4.6).
It is important to mention that the quality and quantity of lac are directly related to the lac host plant. Recently, instead of only Kusum plant, Ber, Siris and Semialata have also been identified as good hosts for Kusmi brood lac.
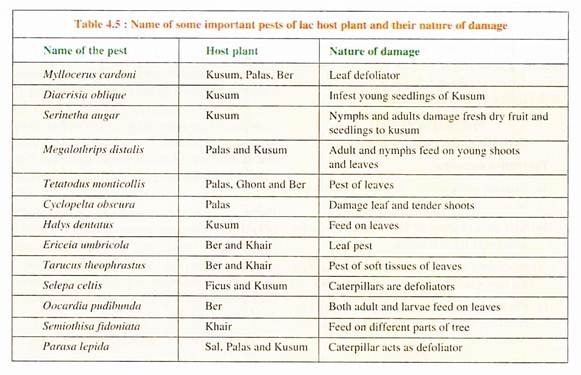
Lac insects require plant species for survival. More than 400 lac host plants have been observed to carry lac insects throughout the world. Besides lac insects which thrive on the sap of known host plants (Table 4.5), a number of other insects also feed on them and directly consume various vegetative and floral parts from those plants.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
These insects act as pests and cause not only damage to the lac hosts but also offer direct competition to the lac insects by devitalizing the host trees resulting into decreased production of lac of commerce. Some pests of lac hosts have been known to inflict very serious damage in seasons of serious outbreaks. Some common and important pests of lac host plants, their nature of damage are listed in Table 4.5.
Control of host plant pests is a complicated problem because of close association of lac insect with its host and its sedentary and colonial habit. Again, lac insect, its own pest as well as the pest of host plants live very close to each other.
So the convenient pest control technologies available till date are not applicable to suppress the pest population either on the host or on lac insect, because the common insecticides in generally recommended doses while killing the pests, may also prove extremely detrimental to the lac insect. So the selection of insecticides, their application and doses should be very judicious.
After exhaustive experiments on control aspects of pests of lac host plants, following are recommended:
Aqueous solution of 0.01 to 0.3% Endrex-20 EC, Aldrex-30 EC, Dieldrex-18EC, BHC 50% WP. Chlordane-65% dust, DDT-25 and 50 EC, DDT-50% WP and Endosulfan-35 EC have been used for control of most destructive pests of host plants.