The following seven points highlight the classification of Platyhelminthes: 1. Polystoma Classification 2. Fasciola Classification 3. Schistosoma Classification 4. Paramphistomum Classification 5. Echinococcus Granulosus Classification 6. Dipylidium caninum Classification 7. Cotugnia Classification.
Type # 1. Polystoma Classification:
Phylum: Platyhelminthes Aceolomate, organ grade and flatworm.
Class: Trematoda Ecto-or endoparasitic; body well without epidermis and cilia, well-development suckers present.
Order: Monogenea Oral sucker weak or absent; anterior end with a pair of adhesive structure; posterior end with an adhesive disc with hooks. Life cycle is completed on one host only.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Genus: polystoma
Comments:
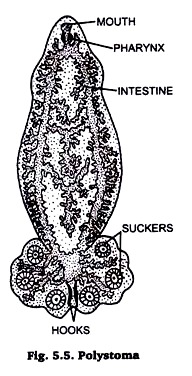
1. Polystoma (Fig. 5.5) is leaf-like and dorso-ventrally flattened.
2. Anterior end is provided with a weak oral sucker.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
3. Mouth is surrounded by the oral sucker.
4. Pharynx is muscular and leads into the bifurcated intestine which finally unit posteriorly. Both the branches of intestine also join each other by transverse connections.
5. Posterior disc or opisthaptor is expanded and contains three pairs of large suckers and 2 or 3 hooks.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
6. Hermaphroditic Male reproductive organs consist of single testis, a vas deferens and a penis. Female system comprises single ovary, oviduct, two vaginae and longitudinal vitelline ducts.
7. Breeding season starts in spring.
Habit and habitat:
Polystoma is found in the urinary bladder of frogs and turtles.
Type # 2. Fasciola Classification:
Phylum: Platyhelminthes Aceolomate, organ grade and flatworm.
Class: Trematoda Ecto-or-endoparasitic; body wall without epidermis and cilia, well-developed suckers present.
Order: Monogenea Endoparasitic, mostly with two suckers without hooks. Life cycle is completed on two hosts.
Genus: Fasciola
Species: Hepatica
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Comments:
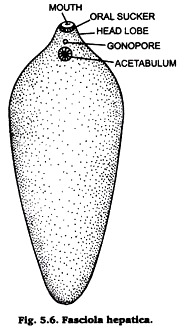
1. Fasciola hepatica (Fig. 5.6) is commonly known a sliver fluke.
2. Body is leaf-like, dorso-ventrally flattened, measures 25-30 mm in length and 4-5 mm in breadth.
3. Anterior end is small and conical, while the posterior end is large more rounded in front than behind.
4. Anoral sucker’ is situated apically and a large highly muscular ventral sucker(acetabulum) is located a little posterior to the oral sucker.
5. Mouth is situated at the anterior end and is surrounded by the oral sucker.
6. Digestive system is simple,pharynx is muscular, oesophagus short and branched and diverticulitis intestine.
7. Between the oral and ventral sucker is a median genital pore through which pass eggs to the exterior.
8. Excretory pore lies at the extreme posterior end of the body.
9. Hermaphroditic Male system consists of testes, vasa deferentia, seminal vesicles, ejaculatory duct and penis, while female system comprises of ovary, uterus and vitelline glands.
10. Life cycle is complicated includes an intermediate host. Limnaea (a mollusc-fresh water snail).
11. Liver fluke causes a disease known as liver rot.
Habit and habitat:
Fasciola hepatica is found as an endoparasite in the bile ducts or liver of sheep.
Type # 3. Schistosoma Classification:
Phylum: Platyhelminthes Characters same as those of Fasciola.
Class: Trematoda …….. –do-
Order: Digenea
Genus: Schistosoma
Comments:
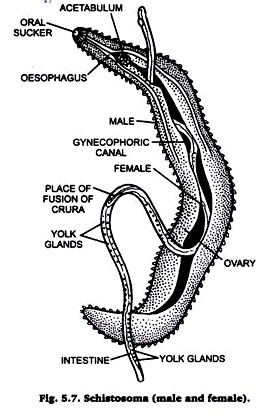
1. Schistosoma (Fig. 5.7) is commonly called the blood fluke.
2. Body long, slender in form and greyish or pinkish in colour.
3. Sexes are completely separate.
4. Male is usually 8 to 16 mm in length, has a cylindrical stout and flattened body.
5. Female is longer than male, usually 15 to 20 mm in length, has a more slender delicate cylindrical body.
6. Males carry females permanently in their gynecophoric canals formed by the in-folding of the ventral body wall.
7. Life cycle includes a secondary host which is Bulinus or Planorbis (a mollusc, fresh water snail).
8. Its infection causes a disease called schistosomiasis.
9. Its 3 species are: S. haematobium, S. mansoni and S. japonicum.
Distribution:
Schistosomes have been reported from Africa (particularly form Egypt), West Indies, South America, Japan, China, Celebes and Philippines.
Type # 4. Paramphistomum Classification:
Phylum: Platyhelminthes
Class: Trematoda Characters same as those of Fasciola.
Order: Digenea
Genus: Paramphistomum
Comments:
1. Paramphistomum (Fig. 5.8) is small, triangular in shape and dorsoventrally flattened.
Fig. 5.8. Paramphistomum:
2. The oral sucker is absent.
3. The ventral sucker is large, muscular and situated posteriorly. It acts as an adhesive organ.
4. It is called amphistome parasite, because acetabulum is large and is found near posterior end of the body.
5. The intestine is forked and un-branched.
6. The male system comprises of two testes with tandem arrangement, sperm ducts, seminal vesicle and cirrus.
7. The female system comprises of ovary, ootype, vitellaria and folded uterus.
8. The genital antrum lies just beneath the fork of intestine.
9. The eggs are large.
10. The lymphatic system is present.
Habit and habitat:
Paramphistomum is an endoparasite in the remen of sheep, goat, deer, cattle, etc.
Distribution:
It is reported from India, Sri Lanka, Burma, other parts of Asia, Europe and U.S.A.
Type # 5. Echinococcus Granulosus Classification:
Phylum: Platyhelminthes Cestoda
Subclass: Eucestoda
Order: Taenioidea
Family: Taeniidae
Genus: Schistosoma
Comments:
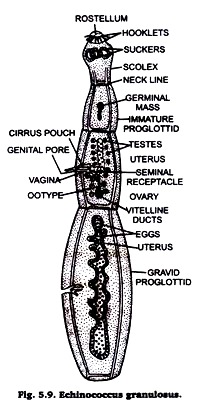
1. Echinococcus granulosus is commonly called dog tapeworm.
2. The worm is only 2-8 mm in length and consists of ascolex, neck and three or four successive large segments (proglottids).
3. The scolex or head bears four suckers and a protrusiblerostellum provided with double rows of 30 to 36 hooks.
4. Proglottids are usually three, first proglottis is generally immature, second proglottis is mature, while the third is large and gravid.
5. It is hermaphrodite. Male reproductive system consists of spherical testes, vas deferens and cirrus. Female reproductive system comprises of ovaries, oviduct, vitellaria, ootype, uterus and vagina.
6. Its gravid proglottis is elongated containing branched uterus with onchospheres.
7. Its infection in man occurs by playing with infected dogs and sometimes the infective onchosphere also reach to man’s body along with food or drink.
8. Hydatid cyst or larval stage occurs in man and other domestic animals, e.g., monkey and cattle.
9. Echinococcus is cosmopolitan in distribution specially in cattle and sheep raising areas.
10. Its hydatid cysts are harmful to man; the cystic fluid is toxic and causes vomiting, diarrhoea, abdominal pain, eosinophilia, etc.
Habit and habitat:
Echinococcus granulosus is an endoparasite in the intestine of dogs, cats and foxes (primary hosts) etc. Its secondary hosts are man, rabbits, kangaroos, sheep and cattle.
Distribution:
Cosmopolitan, especially found in sheep and cattle raising areas. Its infection has been reported from Australia, Japan, India, New Zealand, China and U.S.A.
Type # 6. Dipylidium caninum Classification:
Phylum: Platyhelminthes
Class: Cestoda Characters same as those of Taenia solium.
Subclass: Eucestoda
Order: Taenioidea
Family: Dilepididae Rostellum retractile with one or more circlets of hooks.
Genus: Dipylidium
Species: caninum
Comments:
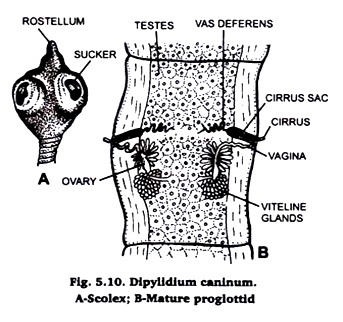
1. Dipylidium caninum (Fig. 5.10) is commonly called dog tapeworm.
2. It is commonly found in pet dogs and cats but rarely in children.
3. It measures 25 cm in length with about 150 proglottids.
4. Its rostellum is muscular, retractile and bears rose-thorn hooks arranged in four transverse circular rows.
5. Its scolex contains four suckers.
6. Its mature proglottids are long and slender with double sets or hermaphrodite reproductive organs and a genital pore on each lateral margin.
7. Testes numerous scattered throughout proglottid.
8. Uterus reticulate which breaks into uterine capsules containing about 30 embryos or less.
9. Dog-louse and dog-flea are secondary hosts in which systicercoids develop.
Type # 7. Cotugnia Classification:
Phylum: Platyhelminthes
Class: Cestoda
Subclass: Eucestoda
Order: Taenioidea
Family: Davaineidae
Genus: Cotugnia
Comments:
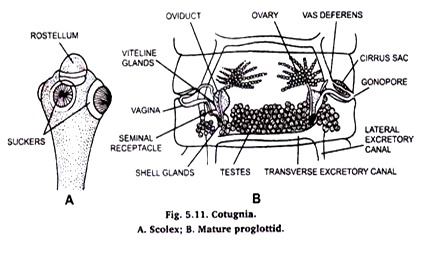
1. Cotugnia is medium-sixed davaineid tapeworm parasitizing pigeon, fowl, duck, peacock, parrot, crow, kite, etc.
2. Tostellum simple with a large number of hammer-shaped hooks arranged in two rows.
3. Scolex bears four spinose suckers.
4. Proglottids bear double set of hermaphrodite reproductive organs (the only davaineid with double set of reproductive organs).
5. Proglottids very short, broader than long except the last ones which are longer than broad.
6. Testes numerous, lie in extravascular field, may or may not cross excretory vessels.
7. Ovaries medially placed.
8. Genital ducts dorsal to excretory vessels and nerve stem.